
AUGUST 24, 2016 | BY WENDY LEVY
Dear Senator Loni Hancock,
I’m writing because “Media Arts” has been specifically excluded from consideration for new arts standards for California in AB 2862, which will delay its inclusion as a formal arts education discipline for at least another generation. This is beyond my comprehension, given California’s historic legacy in its birth and development, its vital “Creative Economy”, and our “multimedia-centered” 21st C society! I have also included Jax Deluca, the Director of the Media Arts Program at the National Endowment for the Arts in this email as well, along with Dain Olson, from the National Coalition of Core Arts Standards andNAMAC Board members and national leaders in youth media and media arts education Kasandra VerBrugghen and Anula Shetty.
As the Executive Director of the National Alliance for Media Arts and Culture (NAMAC), based here in Oakland, I have seen firsthand the power of this unique discipline to change students’ lives, to instill excitement, to empower their voices, and to foster their learning, communicating and creativity. Media Arts is simply magical in its ability to give ALL students a means of expressing themselves in the media that they experience as audiences every day of their lives. This keeps students in school, and helps them to experience writing, research and complex production processes as meaningful and rewarding! Furthermore, it supports their critical awareness of media and digital environments,and prepares them to be participatory and proactive citizens in a democratic society. If you have any doubt about this, the trailer from our recent National Conference is just an inkling of the power of Media Arts in the lives of our young people and our communities: http://namac.org/screening-room/?zoombox=0
Media arts, with its diversifying and complex new virtual and interactive forms, has the potential to foster a new form of cultural and design centered learning, including STEAM, that can propel the next generation to invent innovative solutions for our contemporary challenges. This will empower all of the arts in the next century, and support core instruction in culturally relevant and authentic applications.
Media Arts is endorsed by all national arts organizations and their affiliates (National Coalition for Core Arts Standards, NCCAS) and by other national media organizations, like NAMAC, and the National Association of Media Literacy Education. It has been, or is in the process of being adopted by over 20 states. In California, it is prominently endorsed as a Key Recommendation within State Superintendent Tom Torlakson’s “Blueprint For Creative Schools”.
Please see the attached document, written by Dain Olson, Media Arts Writing Chair, National Coalition for Core Arts Standards, for a more detailed introduction to the discipline and its benefits for students, schools and communities, and its standards-based outcomes for 21 C learning and creativity.
Please join us in supporting the inclusion of “Media Arts Standards” for consideration in the renewal of California’s Visual and Performing Arts Standards for the 21st Century! It is lunacy to exclude the Media Arts from AB-2862.
—
MEDIA ARTS EDUCATION: An Introduction
BY DAIN OLSEN, Media Arts Writing Chair, National Coalition for Core Arts Standards
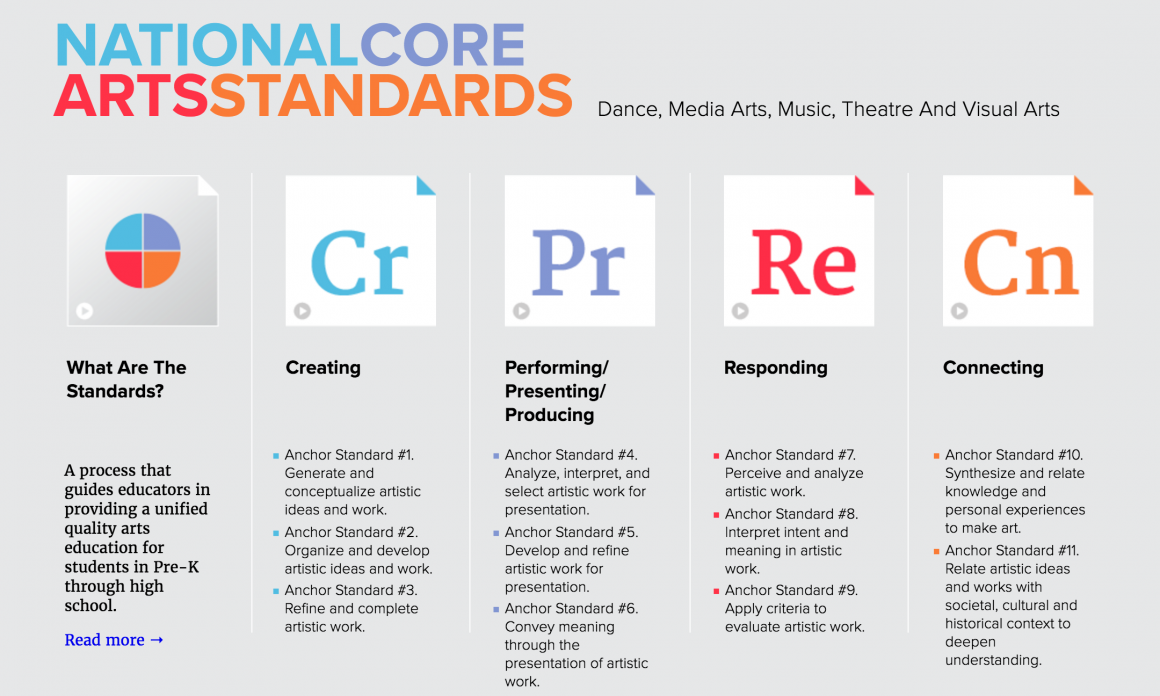
“Media Arts Education” is now recognized at the national level by all national arts organizations and their associates (NCCAS) as a discrete PK-12 arts content discipline in addition to Dance, Music, Theatre and Visual Arts. New National Media Arts Standards have been adopted, or are in the process of adoption by approximately 20 states since their publication in 2014.
We live in a “media arts” centered world. We know and learn about, and create our contemporary world through media arts communications and design formats. Our global culture has moved from text-dominant to multimedia-based modes of perceiving, knowing and communicating, and students should become versed in these processes and literacies for 21st C competence and as participating and media savvy citizens. Furthermore, these tools and methods foster a powerful form of learning that is complex, connective, project-based and real world. Media arts students can apply core academic content in creating cultural products that are meaningful to students and purposeful to their communities.
Media Arts Education encompasses digital arts + interconnectivity across all aesthetic, artistic and academic elements, forms, contents, disciplines and domains, for the purposes of learning and creating. Media arts is intrinsically interdisciplinary, integrative, and student centered around their own culture and interests. Media arts products include: photography, graphics, music, video, animation, motion graphics, web design, interactive apps and game design; 3D products, architecture and environments; radio, TV, internet broadcasting; virtual and augmented reality and virtual worlds, etc.
With this broad range of tools, design processes and production forms, the media arts classroom can form a creative hub within the school; The media arts laboratory is a virtual “makerspace”, where students can produce any communication or expression or design they can imagine, from web sites, movies and sound productions, to 3D designs and games. With advents in interactivity, virtual design and augmented reality, students can produce entire interactive worlds. This form alone can inherently and seamlessly incorporate the highest levels of all mathematics, programming and engineering skills in their authentic application. This is the full realization of the STEAM model.
In media production, students are supported in the investigation of issues that are important to them, and then in creative responses in original communications and designs. In one recent example, the California Alliance for Arts Education has supported students to present their vision for the expenditure of Local Control Funding Formula monies in their local school districts http://studentvoicescampaign.org/. All subject area teachers are encouraged to facilitate student video projects that are then presented to their local school boards. Last year’s pilot model already showed tremendous work and actual results in school board motions. Media Arts Standards guide this challenging process, which integrates writing, media literacy, civic engagement, advocacy, video production and school governance. This supports students in engaging with their local communities and global environment, thereby “dissolving the walls” of the classroom and forming an expanding culture of learning and creative adaptation.
Media Arts Education fosters self-directed learning and ultimately, learning about learning and the full range of 21st C skills. While engaged in these multi-modalities they acquire critical new literacies in media, technology, and digital culture. All Media Arts students are prepared to be effective communicators, creative problem-solvers, collaborators and lifelong learners, as well as for college and career.
—
Media Arts Education
- ● Media Arts Education consists of a unique range of categories including imaging, moving image, sound, interactive and virtual, and their combinations
- ● Media Arts Education has unique aesthetics, principles, tools, processes and pedagogy
- ● Media Arts Education is relevant to young people, as it reflects the multimedia world theycommonly experience
- ● Media Arts Education intrinsically incorporates 21st Century skills and knowledge
- ● Media Arts Literacies (e.g. media, technology, digital culture, aesthetic) are a vital necessity for all young people
- ● Media Arts Education fosters interaction with local and global communities, integration of arts and academics, inquiry into contemporary issues, and the ability to determine effective solutions in multimedia productions and virtual designs
- ● Media Arts Education, as a standards-based arts and design practice for learning and creating, is beneficial for all students and educational institutions
Benefits/Advocacy
Students
- ● Engaging and relevant
- ● Project and Design-based Learning
- ● Arts /Aesthetic /Culturally-centered and Integrated (Holistic)
- ● 21st Century skills and understandings
- ● Student empowering – students as cultural participants and engaged citizens
- ● Adaptive to student interests, pacing, and abilities
- ● “Student-Sourced” – self-generated and directed forms of learning
- ● Multi-literacies (media, tech, aesthetic, digital culture) prepare students think critically in increasingly prevalent, powerful and immersive media environments
Academics
- ● Robust, seamless trans-disciplinary integration across all arts and subject areas
- ● Real world, project-based content application
Schools
- ● Vitalizing school culture (e.g. Digital Yearbook, News Production, Radio and Web Broadcasts, Academic Websites, DJ/VJ Events, Multimedia Theatre)
- ● School to community and global connections and interactions
- ● Integrates and actualizes measurable, high-order, 21st C. learning outcomes – Creativity, Communication, Collaboration, Critical Thinking
Communities
- ● Comprehensive academic and workforce competencies
- ● Civic participation and engagement
- ● 21st C. workforce development
MEDIA ARTS STANDARDS-BASED COMPETENCIES
- ● Meaning Making
- ● Intermodal Orchestration
- ● Expressive Communication
- ● Intentionality/Refinement
- ● Aesthetic Literacy
- ● Critical Analysis
- ● Contextual Awareness
- ● Synthesis/Metacognition
- ● Systems/Digital Culture
- ● Creativity/Imagination
- ● Inquiry/Research
- ● Planning/Organization
- ● Project Management
- ● Design Thinking
- ● Complex Problem Solving
- ● Innovation and Adaptation
- ● Collaboration
- ● Construction/Production
- ● Learning to Learn
- ● Self-Directedness
21st Century Industry Skills
- ● Creative thinking (valued over knowledge)
- ● Innovation – iterative processes that embrace failure and change (play)
- ● Design thinking
- ● Synthesis – integration of multi-disciplines and perspectives
- ● Systems thinking – interconnections
- ● Handle complexity
- ● Can think sequentially and holistically
- ● Flexible – adapt to and analogize for new situations
- ● People who know how to learn
- ● Experience learning for its sake
- ● Breadth of knowledge and interests
- ● Depth of content knowledge
- ● Deep analytical thinking – question everything, including “success”
- ● Problem solving
- ● Effective communications
- ● Integrity, honesty and courage – willing to question convention
- ● Interpersonal skills & teamwork
- ● Professional & technical excellence
- ● Action & results oriented
- ● Ethical reasoning
- ● Entrepreneurial
- ● Fiscally responsible
- ● Project management skills
Contributors:
- LAUSD Media Arts Advisory Committee
- Pixar Animation
- AutoDesk – 2D and 3D Design Software
- ESRI – Geographic Information Systems

Leave a Reply